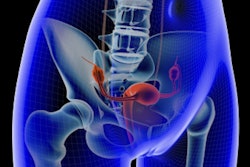
Arterial contrast extravasation on dynamic CT imaging (also known as 4DCT or dynamic volume CT) appears to be an effective diagnostic indicator for postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) cases resistant to conventional treatment, researchers have reported.
The results indicate that this CT finding is a "distinct and common pathology in severe PPH and [is] associated with the need for interventional procedures," according to a team led by Munekage Yamaguchi, MD, PhD, of Kumamoto University in Japan. The group's work was published May 23 in JAMA Network Open.
PPH is a leading cause of maternal mortality around the world, "accounting for 8% of maternal deaths even in developed regions," the group explained. Traditional diagnosis of PPH consists of quantifying blood loss, but this can be tricky and can delay crucial interventions, the team noted. Traditional interventions include uterotonics, balloon tamponade, or coagulopathy correction.
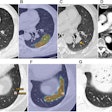
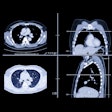
Yamaguchi and colleagues sought to determine the prevalence and clinical implications of PPH by using dynamic CT to identify any arterial contrast extravasation into the uterus.
The group conducted a study of 352 PPH cases identified from 43 Japanese facilities between January and December 2021. A diagnosis of PPH consisted of blood loss exceeding 2,000 mL or requiring more than 10 units of red blood cell transfusion. The study's primary outcome was the prevalence of arterial contrast extravasation on dynamic CT and its association with the need for uterine artery embolization.
Of the 352 patients, 205 (58.2%) underwent CT imaging, and arterial contrast extravasation was identified in 58 of these (32.2%).
The group reported the following:
- Patients with arterial contrast extravasation on dynamic CT had significantly higher total blood loss compared with those without (median 3,455 mL compared with 2,500 mL).
- More patients with arterial contrast extravasation on dynamic CT required uterine artery embolization compared with those without (50 of 58 patients, or 86.2%, vs. 35 of 122 patients, or 28.7%), as well as transfusions.
- Arterial contrast extravasation on dynamic CT was the main factor associated with the need for uterine artery embolization (odds ratio, 27.7, with 1 as reference).
The takeaway? Dynamic CT imaging "should be considered as an essential diagnostic tool in managing treatment-resistant PPH cases," the investigators concluded.
The complete study can be found here.