The latest multimodal large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable progress on radiology board exam questions, according to researchers.
In an experiment with eight LLMs tested on the Japan Diagnostic Radiology Board Examination (JDRBE), OpenAI o3 and Gemini 2.5 Pro performed the best, and received good legitimacy scores from human raters, noted lead author Yuichiro Hirano, PhD, of the University of Tokyo, and colleagues.
“Since our last report in June 2024, LLMs have significantly improved their accuracy and legitimacy on JDRBE. ... Particularly, OpenAI’s o3 and Google DeepMind’s Gemini Pro 2.5 achieved a substantial leap in performance,” the group wrote. The study was published on September 12 in the Japanese Journal of Radiology.
So far in studies, publicly available LLMs have passed text-based radiology exams in multiple countries, yet their image interpretation capabilities have not proven very impressive, according to the group.
However, in early 2025, multiple new multimodal LLMs were released by major vendors. Some of these, such as OpenAI o3, OpenAI o4-mini, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Pro, are “reasoning models” designed to solve complex tasks, the researchers noted. GPT updates (GPT-4.5 and GPT-4.1) were also released.
In this study, with the addition of previously released GPT-4 Turbo and GPT-4o, the researchers tested these models to determine whether they have improved. The dataset comprised 233 questions with 477 images (184 CT, 159 MRI, 15 x-ray, and 90 nuclear medicine images) from the JDRBE from 2021, 2023, and 2024, with ground-truth answers established through consensus among multiple board-certified diagnostic radiologists.
Each model was evaluated under two conditions: with images (vision) and without (text-only). Finally, two diagnostic radiologists with two and 18 years of experience independently rated the legitimacy of responses from four of the models (GPT-4 Turbo, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, OpenAI o3, and Gemini 2.5 Pro) using a five-point Likert scale.
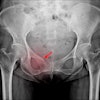
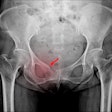
 Question 4 from the Japan Diagnostic Radiology Board Examination 2024, representing a clinical scenario of a man in his 30s presented with transient dysphasia. The question asks to identify the most probable diagnosis from the following options: (a) glioblastoma, (b) hemangioblastoma, (c) metastatic brain tumor, (d) oligodendroglioma, and (e) primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). The correct answer is (d) oligodendroglioma. The figure also includes a summary of responses from four large language models, along with their legitimacy scores rated by diagnostic radiologists.Japanese Journal of Radiology
Question 4 from the Japan Diagnostic Radiology Board Examination 2024, representing a clinical scenario of a man in his 30s presented with transient dysphasia. The question asks to identify the most probable diagnosis from the following options: (a) glioblastoma, (b) hemangioblastoma, (c) metastatic brain tumor, (d) oligodendroglioma, and (e) primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). The correct answer is (d) oligodendroglioma. The figure also includes a summary of responses from four large language models, along with their legitimacy scores rated by diagnostic radiologists.Japanese Journal of Radiology
According to the results, under the text-only condition, OpenAI o3 topped the list with an accuracy of 67%, and achieved the highest accuracy with the addition of image input at 72%.
In addition, image input significantly improved the accuracy of two other models (Gemini 2.5 Pro and GPT-4.5), but not the others, the researchers reported. Both OpenAI o3 and Gemini 2.5 Pro received significantly higher legitimacy scores than GPT-4 Turbo and Claude 3.7 Sonnet from both raters.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study that showed that the addition of images achieved a statistically significant accuracy improvement in the JDRBE,” the group wrote.
The authors noted that according to OpenAI, reasoning models “think before they answer” and generate a long internal chain of thought before responding to the user. However, although reasoning models tended to perform better in this study, the group said they could not conclusively determine whether this was truly owing to their reasoning ability or simply due to increased knowledge.
“Recent LLMs, particularly [OpenAI] o3 and Gemini 2.5 Pro, demonstrated improved accuracy and legitimacy, reflecting notable advancements in their abilities,” the researchers concluded.
The full study is available here.