PET/CT imaging for radiotherapy planning using RefleXion's X1 system appears feasible in patients with prostate cancer, researchers have reported.
A team of radiation oncologists at the City of Hope in Duarte, CA, found that the system visualized tumors for planning in 18 out of 20 patients with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-avid tumors.
“[Biology-guided radiotherapy] using targeted PET radiopharmaceuticals to guide radiotherapy represents a promising new dimension in radiation oncology and warrants further investigation,” noted lead author Bo Liu, PhD, and colleagues. The study was published September 15 in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
RefleXion’s X1 is a medical radiotherapy system that combines a linear accelerator with a PET/CT scanner in an oversized gantry. The system enables real-time dynamic guidance of radiation therapy directed at sites of cancer and has the potential to deliver radiotherapy to a smaller volume with greater sparing of normal tissue, the authors explained. The technique is referred to as biology-guided radiotherapy (BgRT), they added.
In this study, the group aimed to better assess the performance of the X1’s PET imaging subsystem for detecting F-18 DCFPyL PET radiotracer (Pylarify, Lantheus) signals as a foundation for BgRT treatment planning and delivery in future studies.
The researchers recruited 20 patients with prostate cancer who were scheduled to undergo standard diagnostic F-18 DCFPyL PET/CT scans (Biograph Vision 600, Siemens Healthineers). If at least one prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-PET-avid tumor was identified, on the same day, the researchers then scanned the patients on the RefleXion X1 unit. For the analysis, they determined the target volume, activity concentration (AC), and normalized target signal (NTS) and performed BgRT planning.
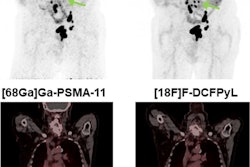
 An example of a typical BgRT plan: A) PET scan on diagnostic PET/CT and B) X1 PET-Linac for patient #15 with a PET avid rib metastasis with GTV size= 3.1 cc, PTV = GTV + 5mm, BTZ (biological tracking zone) = PTV + 5 mm, AC = 14.33 kBq/mL and NTS = 21.04. Red, magenta, and green contours represent GTV, PTV, and BTZ. C) Dose distribution and D) bounded-DVH of a BgRT plan are displayed for the same patient. The bounded Dose-Volume Histogram (DVH) models variations in BgRT delivery, encompassing fluctuation in target background signal variation, target localization and dose delivery uncertainties.Advances in Radiation Oncology
An example of a typical BgRT plan: A) PET scan on diagnostic PET/CT and B) X1 PET-Linac for patient #15 with a PET avid rib metastasis with GTV size= 3.1 cc, PTV = GTV + 5mm, BTZ (biological tracking zone) = PTV + 5 mm, AC = 14.33 kBq/mL and NTS = 21.04. Red, magenta, and green contours represent GTV, PTV, and BTZ. C) Dose distribution and D) bounded-DVH of a BgRT plan are displayed for the same patient. The bounded Dose-Volume Histogram (DVH) models variations in BgRT delivery, encompassing fluctuation in target background signal variation, target localization and dose delivery uncertainties.Advances in Radiation Oncology
However, BgRT was not feasible in 12 (60%) patients due to low target AC (<5 kBq/mL), or low NTS (<2.7) or because of proximity of the PSMA PET-avid tumor to the bladder.
“This pilot study demonstrates the potential feasibility of using F-18 DCFPyL for BgRT on RefleXion unit in patients with prostate cancer,” the researchers wrote.
The group noted that they are planning a larger multicenter trial to confirm these results and generalizability and that potential future applications include targeting lymph nodes, visceral metastases, local recurrences within the prostate bed, and intra-prostatic tumors.
“A larger multi-center study is planned with the goal of obtaining (U.S. Food and Drug Administration] clearance to deliver F-18 DCFPyL-guided BgRT,” the researchers wrote.
The full study is available here.