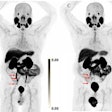
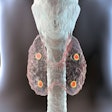
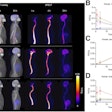
AI can significantly enhance the image contrast of conventional rubidium-82 (Rb-82) PET myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI), according to a study presented September 6 at the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology annual meeting in Orlando, FL.
The finding is from a head-to-head study that compared standard Rb-82 PET MPI, AI-enhanced Rb-82 PET MPI, and PET MPI with the recently approved radiotracer F-18 flurpiridaz in five patients.
“Recent work has shown that AI-generated parametric myocardial blood flow maps with Rb-82 can lead to significant improvement of image quality,” presenter Eric Moulton, PhD, of Jubilant Radiopharma in Kirkland, Quebec, told attendees.
Rb-82 PET MPI rest and stress tests are currently among the most widely used for evaluating blood flow (perfusion) through the coronary arteries to the heart muscle. The technique assesses patients with suspected or known coronary artery disease. F-18 flurpiridaz is a new tracer approved in 2024 for PET MPI that yields images with higher image quality and defect contrast than Rb-82, Moulton explained.
In this study, Moulton and colleagues assessed whether AI could improve Rb-82 PET MPI and compared it with imaging with F-18 flurpiridaz.
Five patients underwent both rest and stress Rb-82 PET MPI and F-18 flurpiridaz PET MPI scans, with an average interval between the scans of 19 days. The researchers used the PET software FlowQuant to process both sets of static and dynamic images. Next, they used a pretrained ConvLSTM (Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory) neural network model to generate myocardial blood-flow maps from the dynamic Rb-82 images.
To evaluate differences in image quality metrics, for all images, the researchers calculated signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), tissue-to-blood ratio (TBR), and defect severity (DS) based on a standard American Heart Association model that segments the left ventricle into 17 regions. Due to the small sample size, they used repeated statistical tests and post-hoc permutations.
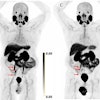
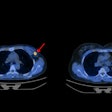
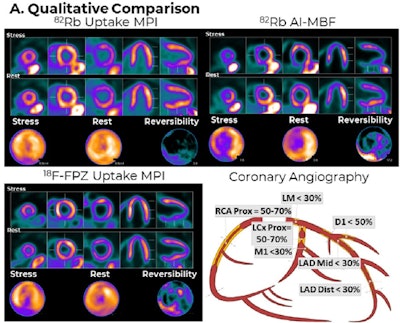 Image comparison between Rb-82 MPI, Rb-82 AI-enabled myocardial blood flow (MBF) parametric mapping, and F-18 flurpiridaz MPI for a representative patient. AI-MBF enhances the defect and image contrast of the uptake image, highlighting areas of reversible ischemia due to moderate disease of the right coronary artery territory more saliently and similar to F-18 flurpiridaz MPI.ASNC and Eric Moulton, PhD.
Image comparison between Rb-82 MPI, Rb-82 AI-enabled myocardial blood flow (MBF) parametric mapping, and F-18 flurpiridaz MPI for a representative patient. AI-MBF enhances the defect and image contrast of the uptake image, highlighting areas of reversible ischemia due to moderate disease of the right coronary artery territory more saliently and similar to F-18 flurpiridaz MPI.ASNC and Eric Moulton, PhD.
“Qualitatively, Rb-82 AI-MBF improved the visualization of reversible ischemia similar to F-18 flurpiridaz,” Moulton noted.
Based on the study, Moulton and colleagues suggested that Rb-82 AI-enhanced MBF imaging significantly enhances image contrast of conventional Rb-82 MPI and reaches the quality of F-18 flurpiridaz MPI. The AI technique could potentially increase sensitivity to clinically significant disease, yet larger comparative studies will be needed to determine the added diagnostic value of in this setting, the researchers concluded.